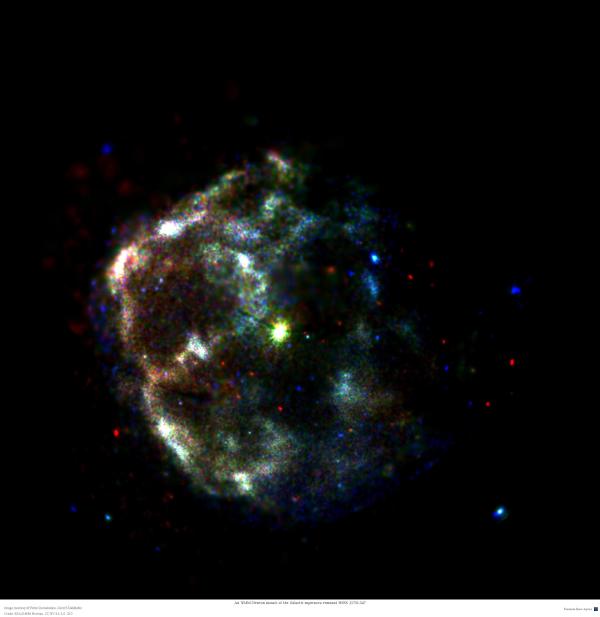
An XMM-Newton mosaic of the Galactic supernova remnant HESS J1731-347
Minimum credit line: Image courtesy of Victor Doroshenko, Gerd Pühlhofer and ESA. (for details, see Conditions of Use).
Credit: ESA/XMM-Newton, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO
The image above can be displayed at full size and may be downloaded by clicking the image above.
| About this Image |
|---|
The X-ray false-color image depicts the Galactic supernova remnant HESS J1731-347 observed with the XMM-Newton EPIC cameras. The extended, filamentary supernova remnant is the result of the explosion of a massive progenitor star. The bright source in the center is classified as the neutron star that remained after the explosion of the massive progenitor star as well. The neutron star has a purely thermal spectrum, i.e. the X-ray photons are emitted at the hot surface of the cooling neutron star. In contrast to that, the extended diffuse emission from the supernova remnant is purely of non-thermal origin, which means that the X-ray glow of the remnant is dominated by emission from relativistic electrons that are accelerated in the shocks of the expanding remnant. The RGB image is colour coded as red (0.4-1.8 keV), green (1.8-2.8 keV) and blue (2.8-10 keV). The remnant is seemingly getting dimmer from East to West (left to right in the image), and the emission appears more blueish (i.e. "harder") in the West. This is interpreted to be mainly due to absorption by a foreground molecular cloud, which is removing lower energy ("softer") X-ray photons predominantly from the Western part of the remnant.
Investigator(s): Gerd Pühlhofer, Victor Doroshenko, Fabio Acero, Dmitry Klochkov, Aya Bamba, and Wenwu Tian
| For More Information |
|---|
- Detailed description of this image
- Query XSA archive for XMM-Newton data in the field of HESS J1731-347
- Astronomical database entries for HESS J1731-347;
- Query SIMBAD for more HESS J1731-347 data
- For unfamiliar terms, visit the XMM-Newton Astronomical Glossary
| Alternate Resolutions | (Help) |
|---|
This image is available in the following downloadable versions: Higher resolution versions of this image may be available, please contact the XMM-Newton HelpDesk.
Search the Image Gallery
To search the Image Gallery for a particular object, fill in the object name in the box below and click the Submit button.To search the Image Gallery for other images, fill in any of the fields below and click the Submit button.
For more search options, please use our Advanced Search form.