Next: 3.2.2 X-ray effective area Up: 3.2.1 X-ray point-spread function Previous: 3.2.1.1 On-axis PSF
The PSF of the X-ray telescopes depends on the source off-axis angle, i.e., its distance from the centre of the field of view (FOV). It also depends slightly on the source azimuth within the FOV. In Fig. 8 the dependence of the shape of the XMM-Newton X-ray PSF on the position within the FOV is presented. One can see that the PSF at large off-axis angles is elongated due to off-axis aberration (astigmatism). The reader is also referred to Figs. 17, 18 and 19 for additional impressions of the off-axis PSF.
For the two EPIC MOS cameras, the PSF is also affected at a level of
a few times 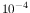 (integral relative intensity) by scattering off
the RGA rib structures. This contribution, however, is negligible in
the vast majority of cases.
(integral relative intensity) by scattering off
the RGA rib structures. This contribution, however, is negligible in
the vast majority of cases.
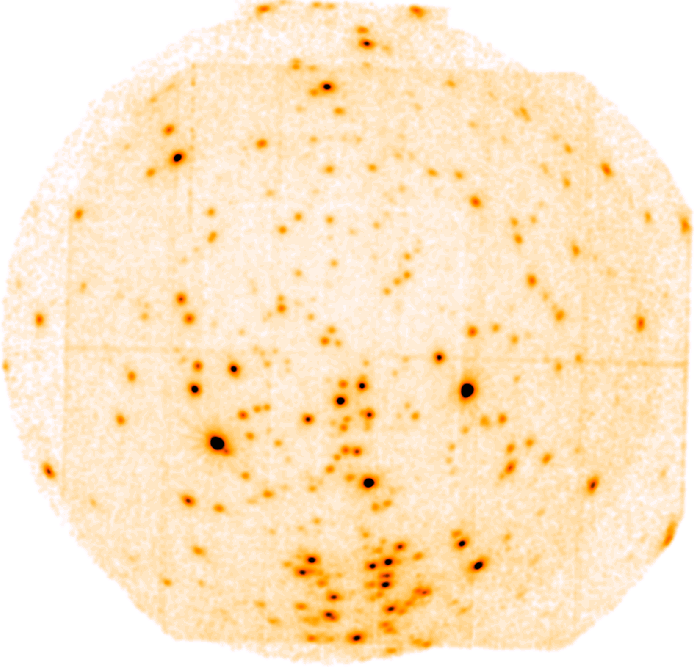
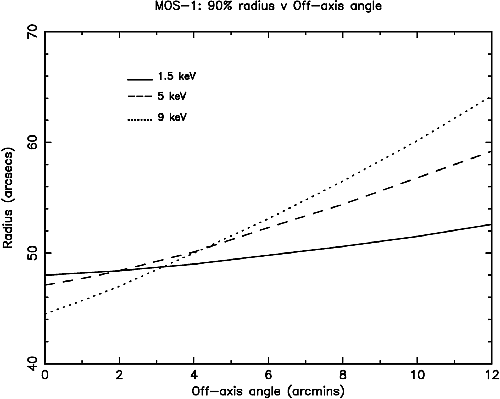
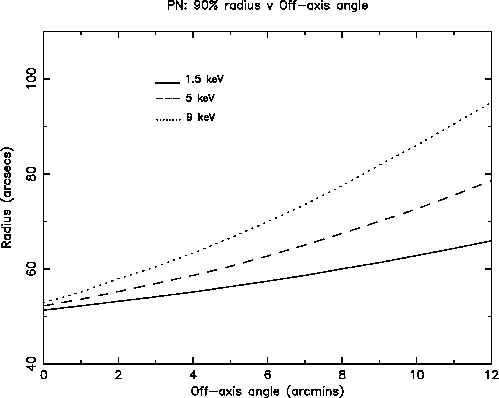
Figs. 9 and 10 show the off-axis angle dependence of the radius at which 90% of the total energy is encircled (W90). As the off-axis angle increases the energy dependence of the PSF changes as focusing of high energy photons is no longer confined to the inner shells. A substantial fraction of these high energy photons are redistributed into the wings of the PSF by X-ray scattering; hence W90 is larger at high energies than at soft energies for large off-axis angles. Note that these data are based on early ray-trace simulations at three discrete energies, and assume a fractional encircled energy of 100% at a radial distance of 5 arcmin, independent of the off-axis angle. For a more precise estimate based on the currently implemented PSF calibration, the user may use the SAS task calview to obtain the encircled energy fraction at a given energy and off-axis angle (note that the "Accuracy Level" should be set to "ELLBETA" through the task interface http://xmm-tools.cosmos.esa.int/external/sas/current/doc/calview/node3.html). Also note that encircled energy correction of point sources is performed by default through the respective SAS tasks (see Section 3.2.3).
Users are referred to Read et al. 2011, A&A, 534, 34 for a comprehensive description of the EPIC PSF, as well as for an empirical characterization as a function of off-axis angle and energy.
 |
 |
 |
European Space Agency - XMM-Newton Science Operations Centre