XMM-Newton
Users Handbook
B. XMM-Newton Routine Calibration Programme
In order to monitor the performance of the XMM-Newton science instruments, regular
observations of a number of targets are performed.
Such observations are defined in the Routine Calibration Plan (available at
http://www.cosmos.esa.int/web/xmm-newton/calibration-documentation#General)
and are used to update the Current Calibration Files (CCFs,
see § 6.2) whenever necessary.
Routine calibration targets are also included in the Target Search Tool
(at URL: http://www.cosmos.esa.int/web/xmm-newton/target-search-tool).
The following monitoring observations are foreseen:
- EPIC
- CTI, Gain and bright Pixel Monitoring: with filter closed or cal-closed
during parts of a revolution when scientific observations
are not possible due to high background radiation. MOS full
frame mode cal-closed data are also collected during slews between
adjacent science targets. Longer observations are scheduled in
parallel to RGS and OM calibration observations. In addition,
diagnostics and noise mode exposures are taken on a regular basis.
Regular observations of N132D were reintroduced in 2013 for the same purpose.
- Effective Area, Gain & Offset Monitoring: preferred target is the SNR
1E 0102.2-7219.
- Detector Response and Redistribution Monitoring: the isolated neutron
star RX J1856.6-3754 is used to monitor these detector characteristics.
- Monitoring of Spectral Capabilities and Contamination: the Vela SNR is observed.
RX J1856.6-3754 is also observed for this purpose.
- Relative and absolute timing Monitoring: based on observations of the
Crab pulsar.
- Stability of the boresight: to be monitored on request, for example
after an eclipse season.
- RGS
- Confirmation of the Wavelength Scale: with AB Dor and HR1099
(replacing Capella due to reduced visibility, as of mid 2016).
- Long-wavelength calibration: with target PSR B0833-45.
- Monitoring of Effective Area: with target Mkn 421 (replacing PKS 2155-304 as of 2015).
- Gain and CTI monitoring: with Mkn 421 at large cross-dispersion offsets (replacing PKS 2155-304 as of 2015),
and (on request) with Sco-X1 on- and off-axis pointings.
- OM
- Monitoring of the Grisms absolute Flux Calibration: observing
the spectrophotometric standard targets GD153 and HZ2.
- Monitoring of the Visual and UV Grisms Wavelength Calibration:
HZ2 is also used for wavelength scale monitoring of the Visible Grism.
- Monitoring of the Photometric Calibration: targets are BPM 16274
and the standard field SA95-42.
- Engineering Mode Observations: are performed whenever OM does not
allow any filter observations but needs to be blocked because of bright
optical sources.
- XMM-Newton Cross-Calibration
In 2003, a major cross-calibration campaign was started to regularly
monitor the internal agreement of the XMM-Newton
detectors and the cross-calibration with other facilities, especially
with the Chandra and NuSTAR X-ray observatories.
- As of 2015, the main cross-calibration target is 3C 273, replacing PKS 2155-304.
Although on previous occasions 3C 273 had been observed simultaneously by Chandra, Suzaku and XMM-Newton,
in recent years the main cross-calibration target was PKS 2155-304 (Ishida et al. 2011, PASJ, 63, 657
discusses the results of this cross-calibration campaign). The data of these observations
are available through the XSA.
The blazar 1ES 1553+113 is used as complementary cross-calibration target.
- XMM-Newton Long-Wavelength Response
The routine calibration task to monitor RGS and EPIC energy
responses is addressed by observations of 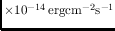 Puppis.
Puppis.
The time needed to fulfil the monitoring requests defined in the routine
calibration plan should stay below a 5% margin of the available time for
science (cf. Policies and Procedures at http://xmm-tools.cosmos.esa.int/external/xmm_user_support/documentation/AOpolicy/).
European Space Agency - XMM-Newton Science Operations Centre
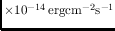 Puppis.
Puppis.